How to configure DBCP connection pool in Hibernate
Due to bugs in the old DBCP code, Hibernate is no longer maintain DBCP-based connection provider, read this Hibernate thread.
Now, Apache DBCP is back to active development, and many bugs are fixed and it’s more stable now. Even Hibernate doesn’t come with connection provider like C3P0 and Proxool, but you still can configure it easily.
In this tutorial, we show you how to integrate Apache DBCP connection pool with Hibernate framework.
1. Get DBCP jars
To integrate DBCP with Hibernate, you need commons-dbcp.jar and commons-pool-1.5.4.jar.
File : pom.xml
<project ...>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>JBoss repository</id>
<url>http://repository.jboss.org/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>3.6.3.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-dbcp</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2. DBCPConnectionProvider
To integrate DBCP with Hibernate, you need to create a “DBCPConnectionProvider” class, refer to this article.
File : DBCPConnectionProvider.java
package com.mkyong.util;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StringWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import org.hibernate.HibernateException;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Environment;
import org.hibernate.connection.ConnectionProvider;
import org.hibernate.connection.ConnectionProviderFactory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class DBCPConnectionProvider implements ConnectionProvider {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(DBCPConnectionProvider.class);
private static final String PREFIX = "hibernate.dbcp.";
private BasicDataSource ds;
// Old Environment property for backward-compatibility (property removed in
// Hibernate3)
private static final String DBCP_PS_MAXACTIVE = "hibernate.dbcp.ps.maxActive";
// Property doesn't exists in Hibernate2
private static final String AUTOCOMMIT = "hibernate.connection.autocommit";
public void configure(Properties props) throws HibernateException {
try {
log.debug("Configure DBCPConnectionProvider");
// DBCP properties used to create the BasicDataSource
Properties dbcpProperties = new Properties();
// DriverClass & url
String jdbcDriverClass = props.getProperty(Environment.DRIVER);
String jdbcUrl = props.getProperty(Environment.URL);
dbcpProperties.put("driverClassName", jdbcDriverClass);
dbcpProperties.put("url", jdbcUrl);
// Username / password
String username = props.getProperty(Environment.USER);
String password = props.getProperty(Environment.PASS);
dbcpProperties.put("username", username);
dbcpProperties.put("password", password);
// Isolation level
String isolationLevel = props.getProperty(Environment.ISOLATION);
if ((isolationLevel != null)
&& (isolationLevel.trim().length() > 0)) {
dbcpProperties.put("defaultTransactionIsolation",
isolationLevel);
}
// Turn off autocommit (unless autocommit property is set)
String autocommit = props.getProperty(AUTOCOMMIT);
if ((autocommit != null) && (autocommit.trim().length() > 0)) {
dbcpProperties.put("defaultAutoCommit", autocommit);
} else {
dbcpProperties.put("defaultAutoCommit",
String.valueOf(Boolean.FALSE));
}
// Pool size
String poolSize = props.getProperty(Environment.POOL_SIZE);
if ((poolSize != null) && (poolSize.trim().length() > 0)
&& (Integer.parseInt(poolSize) > 0)) {
dbcpProperties.put("maxActive", poolSize);
}
// Copy all "driver" properties into "connectionProperties"
Properties driverProps = ConnectionProviderFactory
.getConnectionProperties(props);
if (driverProps.size() > 0) {
StringBuffer connectionProperties = new StringBuffer();
for (Iterator iter = driverProps.entrySet().iterator(); iter
.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iter.next();
String key = (String) entry.getKey();
String value = (String) entry.getValue();
connectionProperties.append(key).append('=').append(value);
if (iter.hasNext()) {
connectionProperties.append(';');
}
}
dbcpProperties.put("connectionProperties",
connectionProperties.toString());
}
// Copy all DBCP properties removing the prefix
for (Iterator iter = props.entrySet().iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iter.next();
String key = (String) entry.getKey();
if (key.startsWith(PREFIX)) {
String property = key.substring(PREFIX.length());
String value = (String) entry.getValue();
dbcpProperties.put(property, value);
}
}
// Backward-compatibility
if (props.getProperty(DBCP_PS_MAXACTIVE) != null) {
dbcpProperties.put("poolPreparedStatements",
String.valueOf(Boolean.TRUE));
dbcpProperties.put("maxOpenPreparedStatements",
props.getProperty(DBCP_PS_MAXACTIVE));
}
// Some debug info
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();
dbcpProperties.list(new PrintWriter(sw, true));
log.debug(sw.toString());
}
// Let the factory create the pool
ds = (BasicDataSource) BasicDataSourceFactory
.createDataSource(dbcpProperties);
// The BasicDataSource has lazy initialization
// borrowing a connection will start the DataSource
// and make sure it is configured correctly.
Connection conn = ds.getConnection();
conn.close();
// Log pool statistics before continuing.
logStatistics();
} catch (Exception e) {
String message = "Could not create a DBCP pool";
log.error(message, e);
if (ds != null) {
try {
ds.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
// ignore
}
ds = null;
}
throw new HibernateException(message, e);
}
log.debug("Configure DBCPConnectionProvider complete");
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = ds.getConnection();
} finally {
logStatistics();
}
return conn;
}
public void closeConnection(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
try {
conn.close();
} finally {
logStatistics();
}
}
public void close() throws HibernateException {
log.debug("Close DBCPConnectionProvider");
logStatistics();
try {
if (ds != null) {
ds.close();
ds = null;
} else {
log.warn("Cannot close DBCP pool (not initialized)");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new HibernateException("Could not close DBCP pool", e);
}
log.debug("Close DBCPConnectionProvider complete");
}
protected void logStatistics() {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("active: " + ds.getNumActive() + " (max: "
+ ds.getMaxActive() + ") " + "idle: " + ds.getNumIdle()
+ "(max: " + ds.getMaxIdle() + ")");
}
}
public boolean supportsAggressiveRelease() {
return false;
}
}
3. Configure DBCP in hibernate.cfg.xml
Now, link your “DBCPConnectionProvider” and define the DBCP properties in “hibernate.cfg.xml“, for example :
File : hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:MKYONG</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">mkyong</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">password</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.default_schema">MKYONG</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.provider_class">
com.mkyong.util.DBCPConnectionProvider
</property>
<property name="hibernate.dbcp.initialSize">8</property>
<property name="hibernate.dbcp.maxActive">20</property>
<property name="hibernate.dbcp.maxIdle">20</property>
<property name="hibernate.dbcp.minIdle">0</property>
<mapping class="com.mkyong.user.DBUser"></mapping>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
The DBCP properties are supported in Hibernate via “hibernate.dbcp.properties-name“.
For all the DBCP properties, please refer to this DBCP configuration page.
4. Run it, output
Done, run it and see the following output :
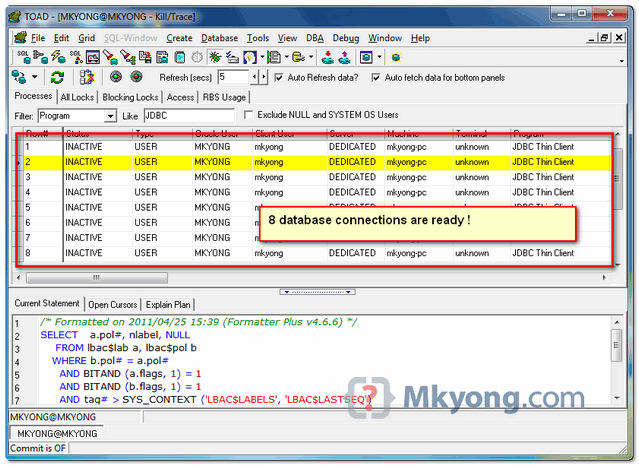
During application start up stage, 8 database connections are created in connection pool, ready for your web application to use it.
Hello mkyong,
good tutorial, I was looking for this.
I have an application running with DBCP on Tomcat 7. I saw that after I Stopped the application, happened an error like this:
GRAVE: The web application [/touchclass] appears to have started a thread named [Abandoned connection cleanup thread] but has failed to stop it. This is very likely to create a memory leak.
Is there relation with this Connection Pool? Have you ever seen this error sometime?
Thanks,
Roni
the material is well made but it will not work properly with never vershions of hibernate, for example 4.3.0, so it is little outdated